Report an Emergency: 203-847-7387
2016 Water Quality Report
Letter to Our Customers
Dear Customer:
Frank N. Zullo, Esq. ChairmanCommissioners, First Taxing District
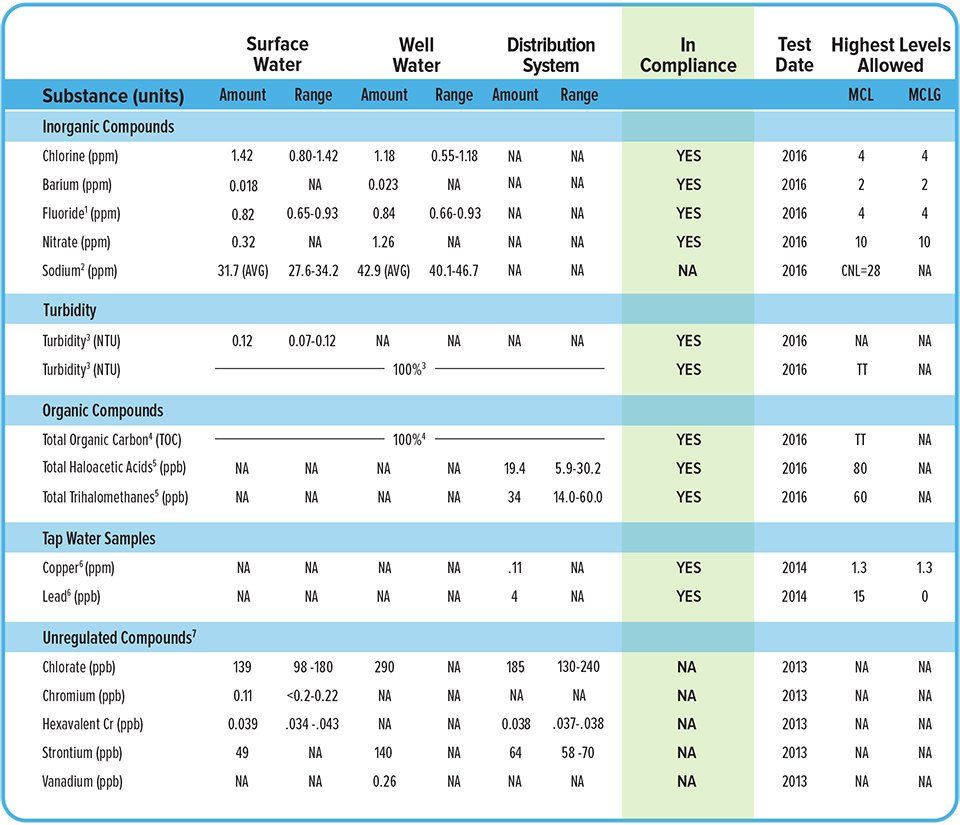
2016 Water Sampling
Footnotes
Acronyms and Definitions
Compound Sources
Request
More Information
About Our Water
How FTDWD Water Is Treated

Water Quality & Sustainability
Water Sources and How We Protect Them
Protecting the water supply at its source is the first step in achieving the water department’s goal of providing safe drinking water to its customers. The District’s reservoirs, located in Lewisboro, NY and New Canaan, CT, hold approximately one billion gallons of water. The source of the water is the watershed land covering 10 square miles in New Canaan, Ridgefield and Wilton, CT and Lewisboro, NY. Rainfall and snowmelt from this land are channeled into soils, groundwater, creeks and streams and then into our reservoirs. Disturbance or pollution on watershed land can directly affect the drinking water reservoirs.
Measures to protect the watershed land and reservoirs include frequent patrolling of the area. Open communications with both the local police and fire departments in our watershed towns is essential. We also work closely with local government focusing attention on new land development in our watershed. When necessary we actively oppose unsuitable development. Each year our water treatment operators visit the properties on the watershed as part of our sanitary survey requirement.
Procedures to protect our groundwater sources in the Kellogg-Deering well field continue through the Aquifer Protection Area Regulations. The Norwalk Zoning Commission has used its authority to register and regulate businesses that pose a potential risk to our drinking water. The commission continues to provide updates to the registrants and work closely with the water department with regard to protection of our well field.
Customer Inquiries
Many customers have asked about the hardness level of our water because dishwasher and hot water heater manuals may ask for this information. Hardness in water is determined by the calcium and magnesium (both nontoxic minerals) content in the water. Our water has a moderate hardness in the range last year of (74-135) mg/L or (4.3-7.9) grains per gallon.
This past winter brought about customer inquiries about cloudy water. All tap water contains dissolved gases primarily air. The colder the water, the more gas it can absorb. When water from the treatment plant enters the distribution pipes, the water is pressurized. Water under pressure holds more air than water that is not pressurized. Once the water comes out of the tap it is no longer under pressure and the air comes out of solution as bubbles. It could look cloudy for a short time.
Lead in water remains in the news as communities try to reduce the chances that lead from plumbing components will end up in the drinking water. The First District’s water is lead-free when it leaves our treatment plant but lead can enter the water as it travels through a lead service pipe, lead solder or household plumbing containing lead. Please contact us if you are interested in testing your drinking water for lead. Please read more about lead under “Lead and Drinking Water” at the end of this report.
Source Water Assessment
A source water assessment performed by the State of Connecticut Department of Public Health indicated that the surface water source has a moderate susceptibility and the groundwater source a high susceptibility to potential sources of contamination. This does not imply poor water quality but does indicate the need for protection. The completed assessment report can be found on the Department of Public Health website.
Additional source water assessment information can be found at the Environmental Protection Agency website at: www.epa.gov/sourcewaterprotection